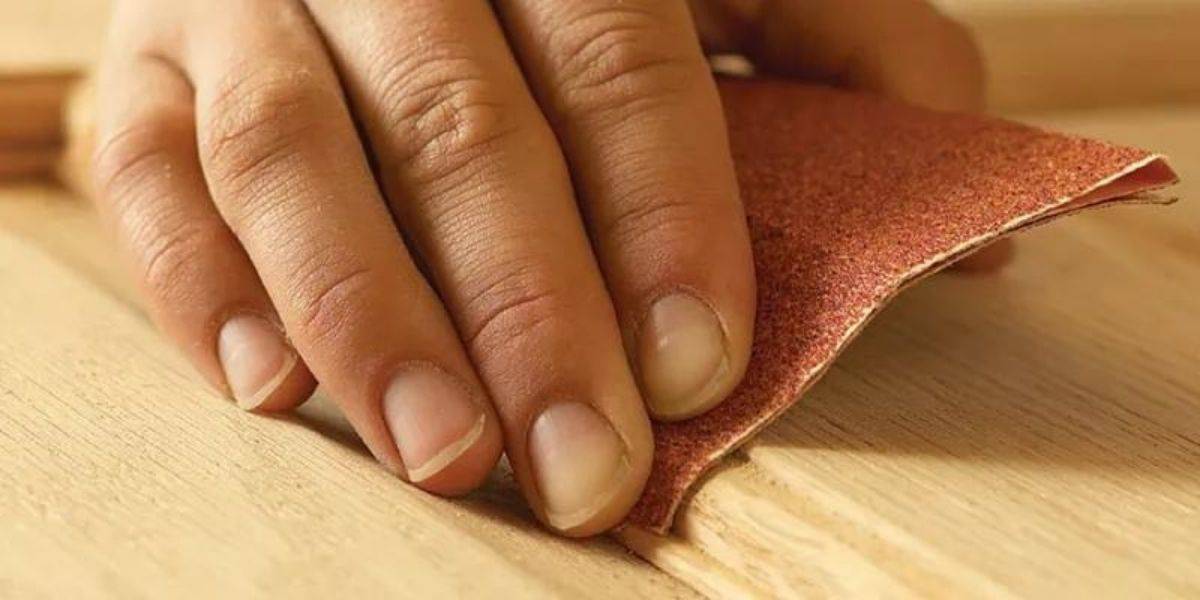
El lijado de superficies planas barnizadas es una operación habitual en la industria de la madera, los tableros y la...
}Performing a perfect job is the goal of every professional. An unpolished finish, with a polished surface, well treated and with all the necessary tools, are fundamental requirements for this. But, to achieve this, it is necessary to know what the elements with which we can work are and know how to differentiate which is better for each occasion.
At Abracom we want to help you in everything within our reach, providing you with all the products you need and with the highest quality guarantee. In addition, we accompany you throughout the process, guiding and advising you on what is best for each of your projects. Therefore, this time we will explain everything about abrasive discs: what they are, the different types, their characteristics...
With this information, when it is time to choose the right abrasion discs, you will know what exactly you need. So, go ahead, keep reading!
What is an abrasive disk?
The abrasive discs are a fundamental piece to be able to use a fixed or portable tool that helps us to cut, roughing or sanding any material, through friction. Its design, shape and composition will vary according to the use that will be given.
In general, its composition is based on a series of crushed abrasive grains, joined together by a binding agent, anchored and fixed to a support material. These grains can be made of natural or synthetic aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, zirconium, ceramic or diamond.
The use of abrasive discs in the secondary steel industry is widespread: from shipbuilding and manufacturing of household appliances, components for the automotive and construction sectors, special profiles, pipes and electrical appliances to maintenance and repair of equipment, tools and machines.
Abrasive discs are a fundamental part of using machine tools for sanding any material
Abrasive cutting discs
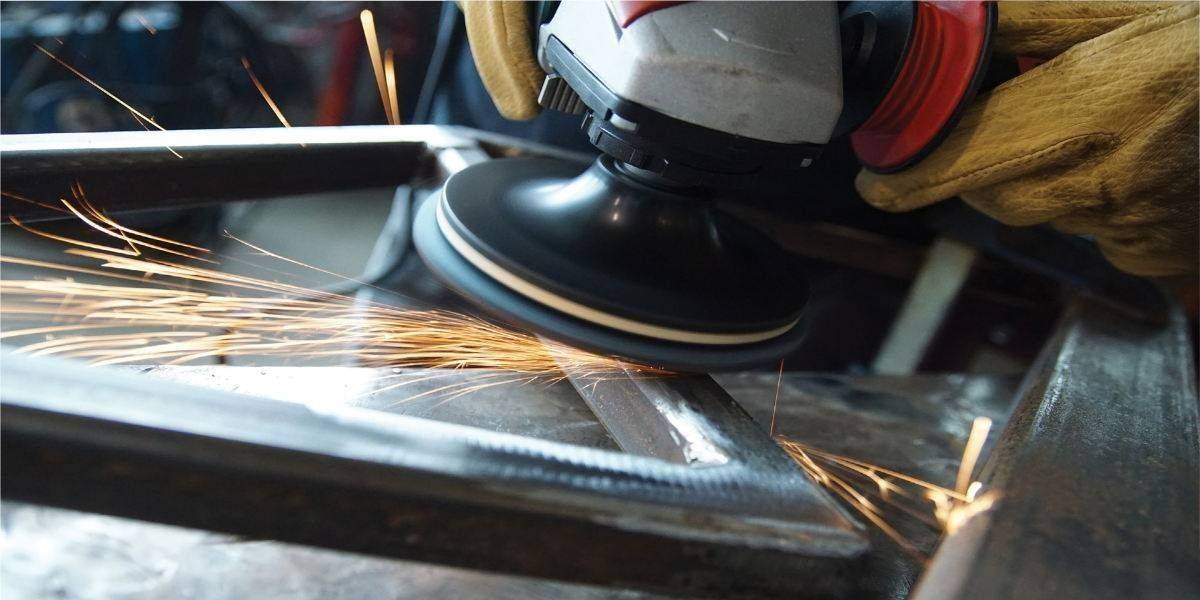
The cutting process is one of the most used in the metal sector. Abrasive disc cutting is the most common, versatile, comfortable and cheap.
In this operation the main factors to consider are: the thickness of the cutting disc, the thickness of the material to be cut, the substrate to be cut, the power of the machine, the pressure exerted and the heat provided.
According to the material of which the disc is made we can find two categories;
The conventional ones: that come from aluminum oxide, silicon carbide or a mixture of aluminum oxide and zirconium. They are ideal for working with soft, hard and semi-hard materials. They are used to cut, rough and polish steel, cast iron, ceramics, copper...
The super-abrasive: in this block the abrasive discs that have to carry out a more intense cut are included. They are used exclusively for cutting and roughing at high speed, and in a very precise way, very hard materials.
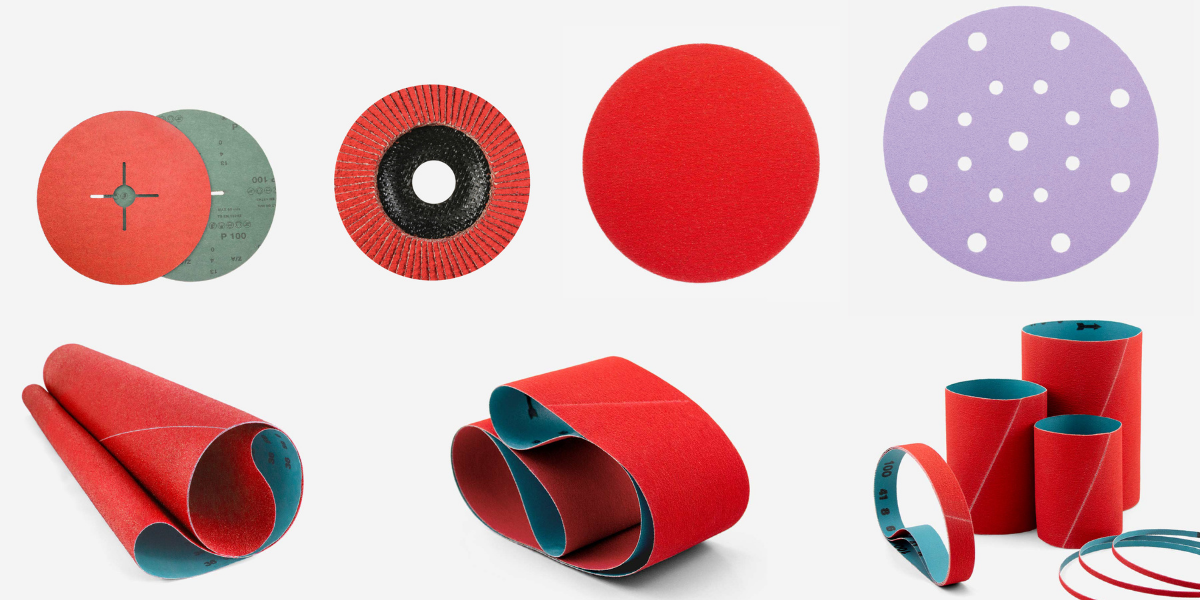
Forms of abrasive discs
According to the shape of the abrasive cutting discs we can classify them in:
Flat cutting discs: they are used for cutting. The diameters vary between 75 and 400 mm for portable machines and 300 to 400 mm for fixed machines.
Concave discs (with depressed center): its use is for cutting, with a diameter of between 75 and 250 mm, and for roughing, where the thicknesses range from 2 to 10 mm and the diameters from 75 to 250 mm for portable machines
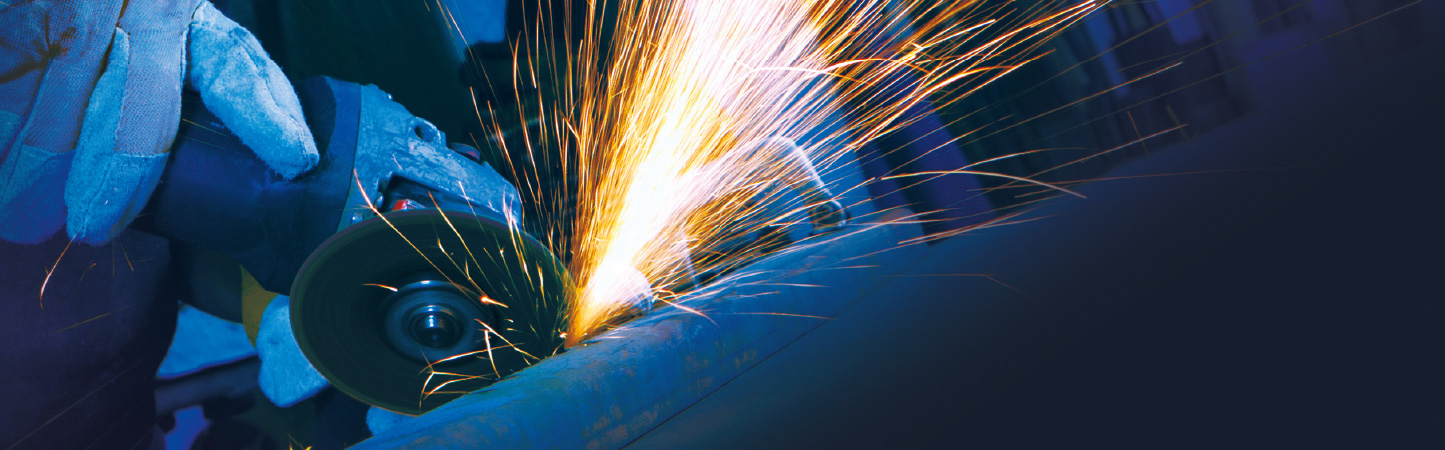

Abrasive grinding discs
The roughing process consists in removing the excess material from a piece to obtain the desired shape and dimensions. The main objective is to eliminate as much material as possible in the shortest possible time, regardless of the finish we are going to obtain.
We must take into account the factors that can affect the performance of the disk: the heat generated, the pressure exerted by the disk on the piece, the speed of work, and the projections of the rest of ore in blocks.
To know more: Abrasives and industrial machinery: products for a perfect finish
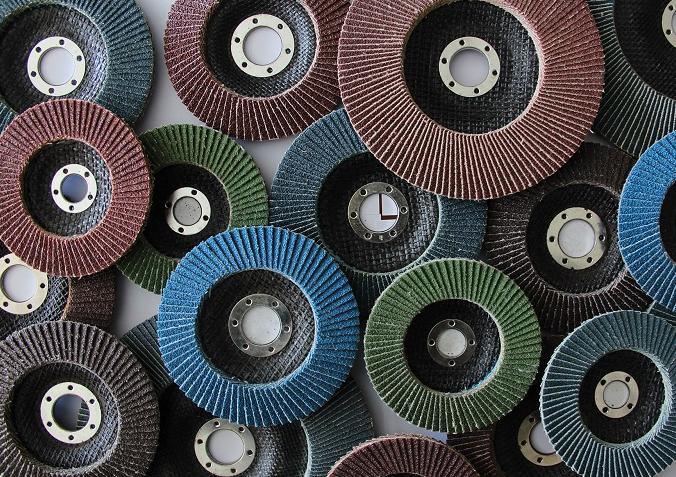
Inside the abrasive grinding discs we find:
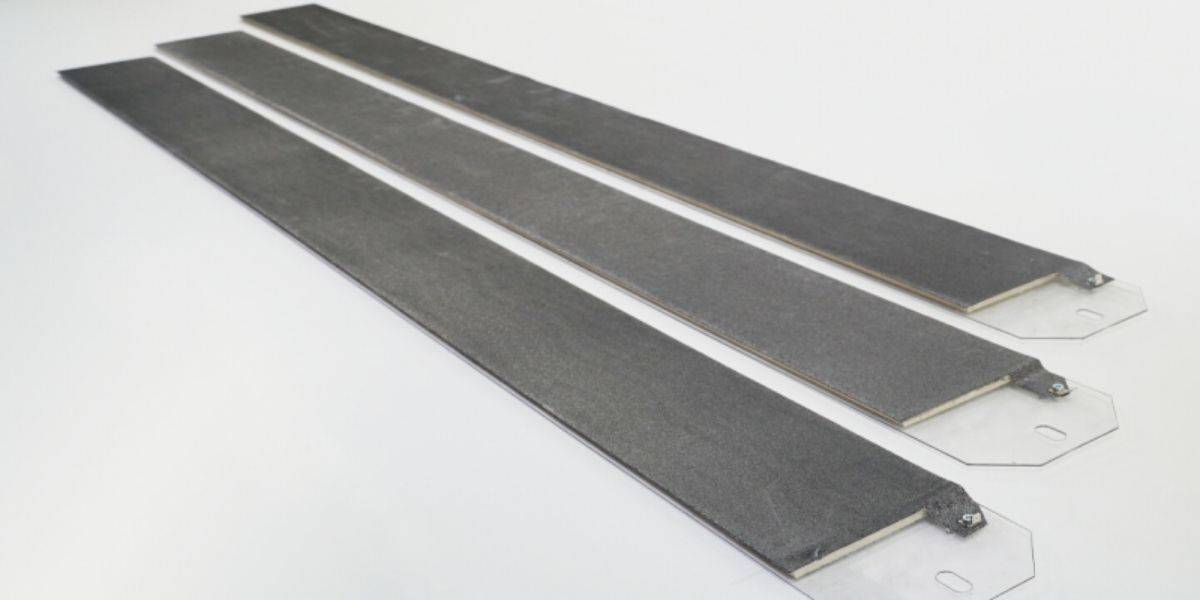
Flap discs, designed for roughing with great performance when the finish is important.
These sandpaper discs are made of sheets of abrasive cloth and fiber. They are available in many forms, abrasive minerals and special coatings to meet the needs of each application.
When the speed in the roughing is the determining factor we will make use of the fiber discs for the roughing of flat pieces.
They achieve a greater elimination of the material in the operations of roughing and deburring. There is a wide selection of diameters, minerals and grain on the market.
Finally, we must consider non-woven discs for the elimination of stainless steel welding. Their high cutting power allows them to eliminate weld seams while leaving a very fine finish that reduces the number of subsequent steps until the final finish of the piece.
They have an open three-dimensional fabric construction that allows a quick cut, keeping the surface cold and without embossment. They facilitate the removal of rust, weld spatter, scale and other surface contaminants.
Abrasive sanding discs
The sanding process consists of those surface smoothing and refining operations performed with abrasives, both in wood, metal, plastics, glass, composites, varnishes, etc ...
In several passes and using thinner grains every time, we can obtain uniform surfaces with different levels of finish. Normally this sanding is done with roto-orbital machines that have a suction system using discs with different amount of holes in their surface.
You may be interested: Basic recommendations for choosing the right abrasive products: rolls, discs and bands

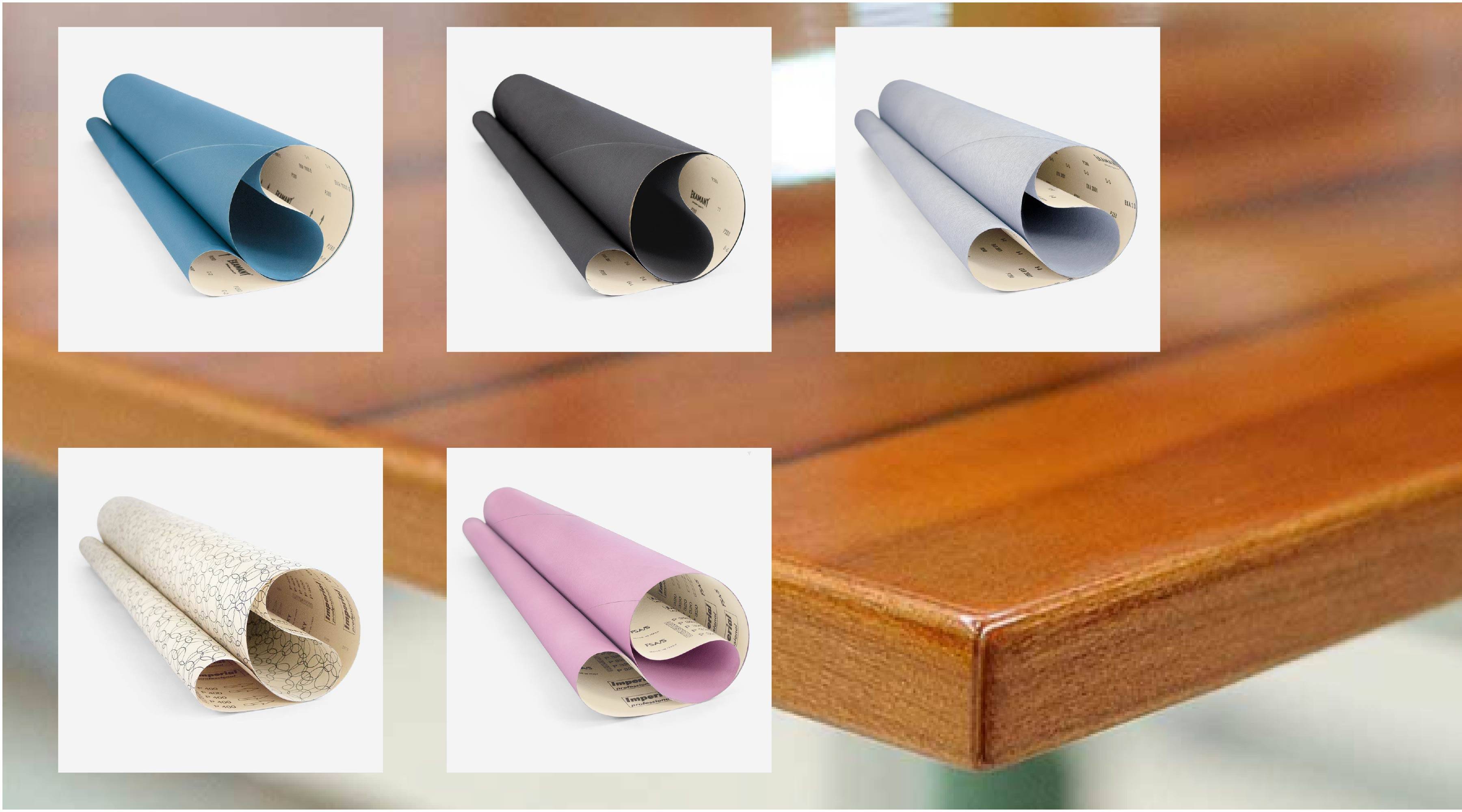
Abrasives used in different abrasive discs
As we have said before, the abrasive materials used for the composition of the disc grains can be of natural or synthetic origin.
Natural abrasives, as the name implies, come from nature itself. The most common is emery composed of corundum and iron oxide. It is used for general polishing of metals in very fine grains.
On the other hand, there are synthetic abrasives. They are high quality materials, such as silicon carbide, aluminum oxide or synthetic diamond. Its manufacture is the result of the mixture of raw materials and chemical element. These types of abrasives are very modifiable, that is, their hardness can be adjusted according to what is needed.
Aluminum oxide is resistant and adapts well to roughing high strength materials such as carbon steel, alloy steel, bronze and hardwood.
Silicon carbide is the hardest and sharpest mineral. It is suitable for sanding non-ferrous metals: aluminum, brass, bronze, magnesium, titanium, ... rubber, glass, plastics, fibrous wood, enamel... Silicon carbide outperforms any other abrasive in terms of its ability to penetrate and cut faster With little pressure.
Zirconium has the quality of self-sharpening that gives it a long service life in hard work of material removal. It is ideal for heavy metal roughing and wood calibration.
Ceramic aluminum oxide is a durable, resistant and dense abrasive. Its grain microstructure allows it to break during roughing, generating multiple new cutting edges. It is normally used in medium-high pressure jobs. It is recommended for carbon steels, forged steels and alloys containing nickel and cobalt.

Safety advice when using cutting discs
Just as work is carried out with precision, care and patience to achieve an impeccable result, it is necessary to remember that operator safety is essential. Next, we will give a series of basic tips when it comes to treating cutting discs.
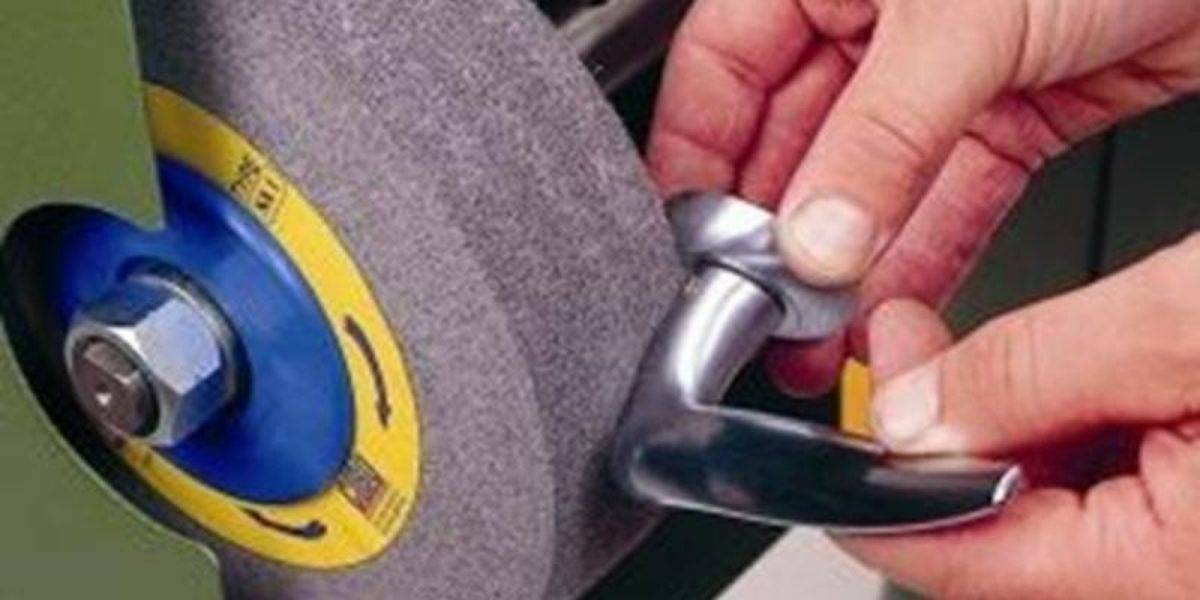
Check the discs, tools and materials with which we are going to work: before changing the abrasive disc that we are going to use in our tool, it is necessary to review, one by one, the discs that we are going to use. If one is damaged, broken or in poor condition, do not use it under any circumstances.
Place them correctly in the machine tool: before starting any work, make sure that the abrasive disc is perfectly positioned and that all the safety elements are correctly arranged. Never force the disc on the machine shaft, or force the mounting or locking flanges, or use any machine that is in poor condition or malfunctions.
If any of the discs we are going to use are damaged, broken or in poor condition, we should not use it. Nor should we ever force the disk into the axis of the machine tool
Ensure that the machine is turned off when not in use: any manipulation of the machine, before or after use, should be done in the off position and, if possible, unplugged from the power outlet.
Follow the manufacturer's instructions: it is essential to always use the tools provided by the machine manufacturer to change the disc. You always have to go at the recommended speed and, under no circumstances, overcome it.
Use proper protection: safety glasses and clothing is mandatory, not only recommended. In addition to gloves, safety shoes, dust masks, ear protection ...
Maintain and handle the tools firmly: it is essential to hold the machine being used tightly. With both hands (in case of larger and heavier machinery) and trying to be as concentrated as possible to avoid possible damage.
You may be interested: Why choose Norton Abrasives products for your company
Throughout the post we have explained everything related to abrasive discs to solve the doubts that normally arise.
At Abracom we have the best quality in abrasive discs and other materials and solutions for professional surface sanding. Do not hesitate to contact us if you have any questions or needs.







.png)














 (1).png)
 (1).png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)







