El lijado de superficies planas barnizadas es una operación habitual en la industria de la madera, los tableros y la...
}Three-dimensional abrasives are generally those that are made on a fiber backing, like a skein of nylon threads that are not woven together. They are commonly known as scotch or non-woven fiber, and stand out for their great damping capacity during sanding operations.
From the point of view of damping during sanding work, we can also include in this family abrasive sponges or pads and abrasives with flexible foam backing. Like the rest of the abrasives, they all consist of mineral grains, binders or adhesives and support material.
Depending on the type of support, we can classify abrasives into: flexible, three-dimensional and liquid:
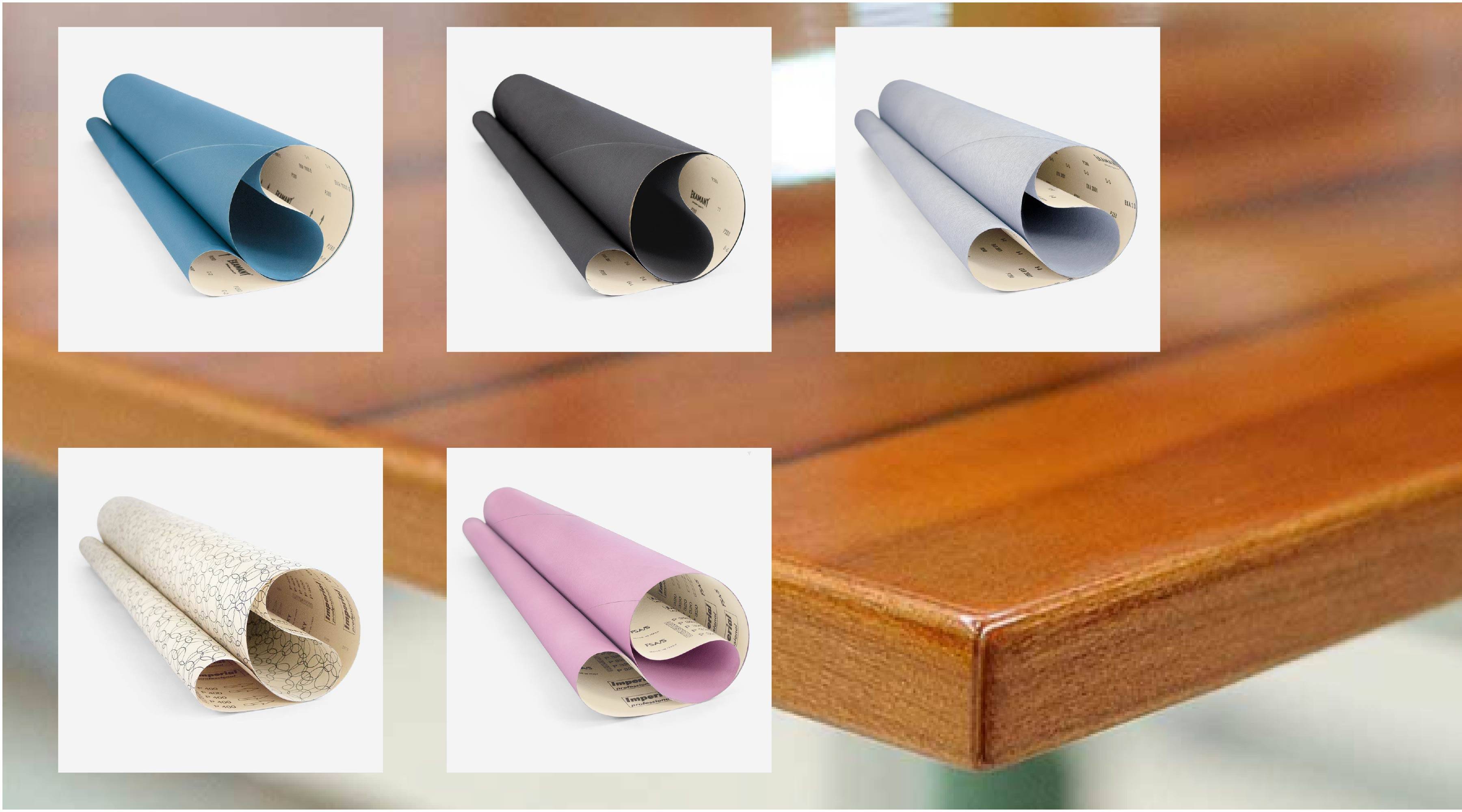
Flexible abrasives are made up of flat supports made of paper, cloth, combination, film and vulcanized fiber.
Three-dimensional abrasives consist of non-woven fiber backings, abrasive pads or sponges, and paper backings with cushioning foam.
Liquid abrasives are made up of abrasive creams, liquids and pastes.
In most work with a three-dimensional abrasive, the support is the differentiating element, which determines the degree of flexibility, resistance to breakage, the ability to adapt to the shape of the pieces and the possibility of being able to work wet.
In three-dimensional abrasives, unlike flexible abrasives, the grain size is not indicated by a specific grain numbering, for example, P240, but by a grade related to the finished level: coarse, medium, fine, very fine, superfine, ultrafine and microfine.
Each manufacturer has tables of equivalences between the different types of abrasives and the different standards for numbering and grain size: FEPA (European), ANSI (American), microns, pyramidal type, ...
At the same time, in the same manufacturer, the different forms of three-dimensional abrasives: sheets, rolls, discs, belts, brushes ... have different equivalences between the size of the grain and the level of finish. This is so because the characteristics and density of the fibers used vary from one format to another.

Types of three-dimensional abrasives
Depending on the shape and structure of these abrasives, we can consider the following formats as the most common:
For hand sanding
Fibrite sheets or sheets.
Fibrite rolls with and without precut.
Abrasive sponges or pads.
Rolls with foam backing with and without pre-cut.
For sanding with a manual sander (orbital, grinder, angle, satinator ...)
Fibrite discs.
Surface conditioning discs.
Semi-rigid clean & strip discs.
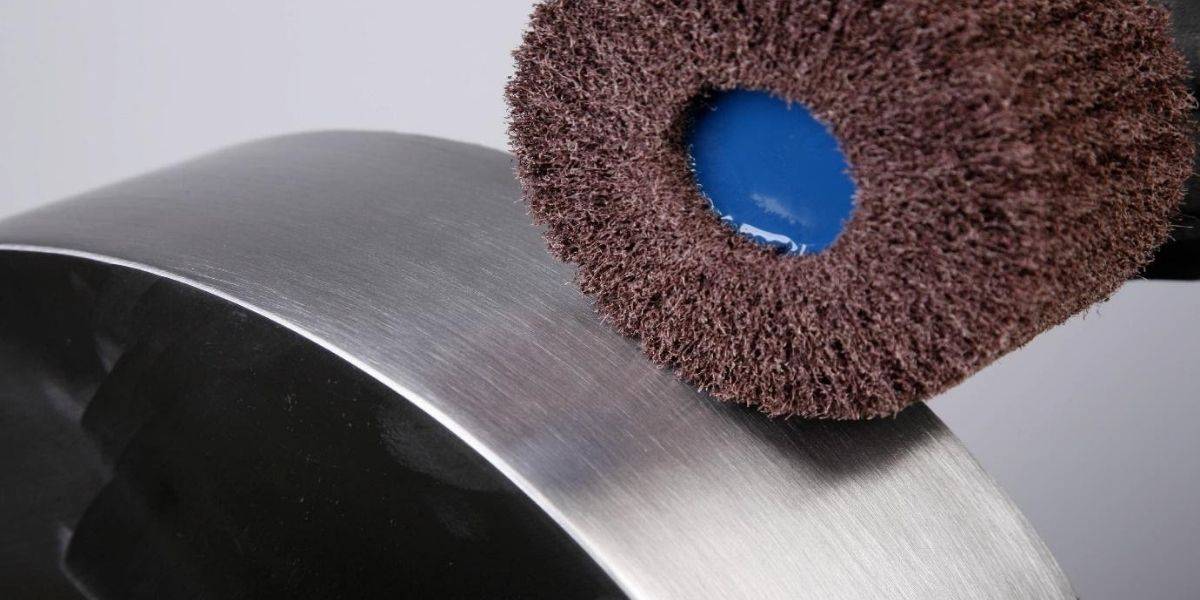
Mini Brushes, Core Brushes and Shaft Brushes
For sanding with a stationary belt sander
Surface conditioning belts: mini belts, sleeves, long belts and wide belts.
Abrasive wheels
Advantages of three-dimensional abrasives
Non-woven fiber abrasives, abrasive sponges, and foam-backed abrasives provide significant advantages over other types of abrasives.
They facilitate the damping of sanding operations during industrial processes in which there are a great variety of manual applications.
They are very flexible, they can be rolled and squeezed so they adapt to the contours, shapes and areas of difficult access.
They achieve a uniform, fine and smooth finish thanks to the optimal distribution of the pressure of the support, eliminating pressure points.
Unlike conventional flexible abrasives, they produce a more satin finish.
They are less affected by the dulling of the abrasive mineral as it is a non-woven fiber with an open structure, which favors less clogging, and an easy evacuation of the remains of the sanded material.
They have a long useful life thanks to the latest manufacturing technologies available.
They are waterproof, washable and reusable.
They can be used on both sides since both sides are abrasive, so they are easy to use.
Main uses of three-dimensional abrasives
Three-dimensional abrasives are generally used for a wide range of applications. They are especially used during cleaning and removal of rust or paint, deburring, cutting edges, eliminating weld spots, cleaning the weld bead, surface preparation, finishing, sanding of moldings, etc.
For hand sanding
Fiber sheets and fiber rolls (with and without precut) are ideal for manual cleaning, finishing, deburring and polishing of metal and painted surfaces.
Abrasive sponges are ideal for hand sanding surfaces, both contoured and flat, wood, paint and metal.
Foam-backed rolls (with and without precut) are perfect for hand sanding around curves, contours and round edges. They facilitate a great finish in primers and topcoats of paint finishes.
For sanding with a manual sander (orbital, grinder, angle, satinator ...)
Like fibrite sheets and rolls, fibrite discs are suitable for surface finishing, shading and polishing.
The surface conditioning discs offer excellent results when cleaning and preparing surfaces. They are ideal for cleaning, light deburring and processing of stainless steel weld beads.
The semi-rigid unitized discs, or rapid strip, facilitate rust removal and excellent adhesion in subsequent coating, painting and welding processes. These discs are used after flap and fiber discs to smooth and obtain an optimal surface finish in one or two operations.
The clean & strip type discs are perfect for stripping, removing sticky or adhesive coatings and cleaning the surface quickly, without producing marks or wear on it.
Brushes made from non-woven fiber sheets (with a core and/or with a shaft) are ideal for finishing large parts and complex shapes. They are less aggressive than conventional sanding brushes with cloth sheets, and can be used with metals, wood, composites and plastics.
For sanding with a stationary belt sander.
The surface conditioning belts, in their different formats, mini belts, sleeves, long belts and wide belts, are ideal for removing scale, surface defects, rust, corrosion, tool marks, lamination marks, bond lines, light burrs, and to give the desired technical finish.
Abrasive wheels are used to remove rust, shine and burrs. Also for reducing surface roughness, smoothing and polishing weld seams, scratching stainless steel and decorative finishes.
At Abracom we are specialists in the treatment of surfaces with abrasives. We have a wide range of flexible and three-dimensional abrasives to provide a solution to the multiple applications of sanding and finishing in the professional sector and industry.






 (1).png)







